|
THINK is probably best known for its Structure-based virtual screening capabilities because it
was used in two major Distributed Computing projects: the Oxford University Cancer project and the Find-a-Drug project.
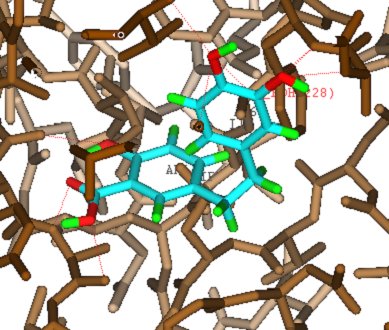
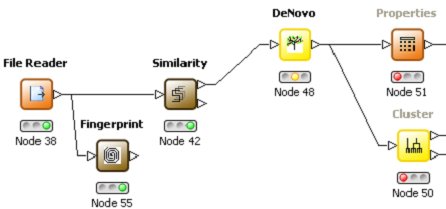
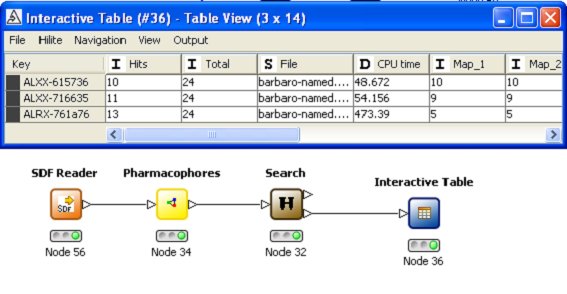
Pharmacophore technology is used matching interaction centres in potential ligands to possible interactions
with the protein residues. A full conformational generation is implemented and an enhanced ChemScore
function is used to score the hits. A comprehensive implementation includes options for the user
to elect to refine side-chain positions, save all docked conformers, visualise the hits etc.
| 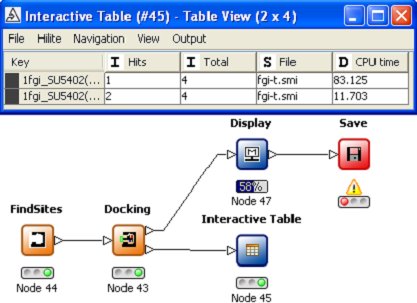
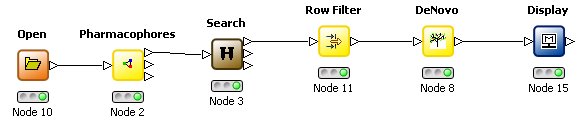
Probably one of the most exciting aspects of using KNIME is the ready automation of tasks which
were previously considered tedious and time-consuming. For instance, if there are several possible
binding sites THINK can automatical locate these from bound ligands; PDB site records or a site search and dock a set of training molecules into each
site summarizing the results in a table. This enables higher quality modelling studies - optimising the
configuration for a training set - to be completed with less effort!
Note:The molecular graphics THINK nodes are currently only released for Windows.
There are third party molecular graphics nodes for Linux.
|